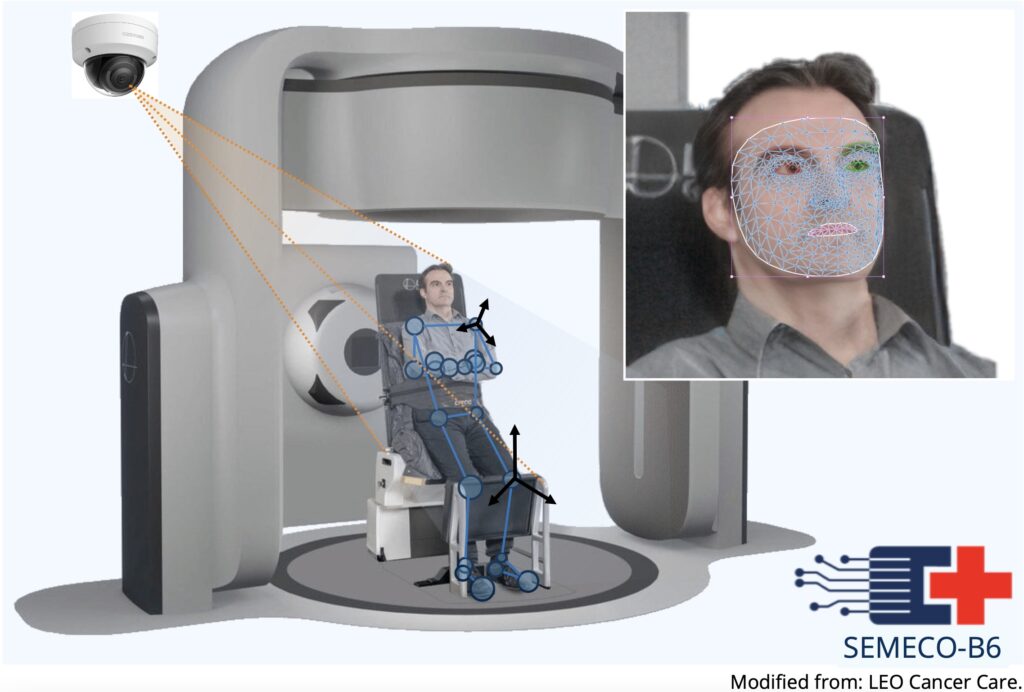
This project aims at introducing wireless positioning aids based on photogrammetric and AI-based techniques in the field of radiotherapy in order to increase efficiency and precision of patient positioning, and to monitor positioning changes during the course of a treatment session.
In radiotherapy, accurate and precise patient positioning is critical to ensure the radiation dose effectively targets the tumour while minimizing exposure to surrounding healthy tissue. Typically, treatment is based on a 3D CT scan that serves as the reference for all sessions, requiring patients to be consistently positioned as during the initial scan. Current methods often rely on immobilization devices like rigid masks, which can be uncomfortable and burdensome for patients.
This project aims to improve patient comfort and positioning accuracy by developing a novel hard- and software prototype for non-invasive, AI-based tracking of patient position changes during radiotherapy. The system includes multiple cameras for image acquisition, AI-based detection of patient positioning, and transformation into a digital 3D space.
At its core, the solution uses a morphable geometric human body model—featuring both outer and inner anatomy—to detect patient posture and location across various treatment setups. The prototype will be validated in collaboration with two industrial partners: Elekta (supine positioning) and LEO Cancer Care (upright positioning).
This innovation aims to enhance treatment precision while reducing patient discomfort during radiotherapy.
Dr.-Ing. Mirko Riedel I deveritec GmbH Dresden
- Dr. med. Dr. Esther G.C. Troost | University Hospital Carl Gustav Carus and Faculty of Medicine Carl Gustav Carus, TUD Dresden University of Technology
- Dr. habil. Hans-Gerd Maas | TUD Dresden University of Technology
- Dr.-Ing. Danilo Schneider | University of Applied Sciences – HTW Dresden